Color
Understanding the color system and its application in your theme.
Radix Themes comes with a number of color scales, each with their own light, dark and alpha variants. Under the hood, the color system is powered by Radix Colors.
Accents
Accent color is the most dominant color in your theme. It is used for primary buttons, links and other interactive elements. accent_color is specified directly on the Theme component:
use radix_yew_themes::{AccentColor, Theme};
use yew::prelude::*;
#[function_component]
pub fn AccentColorExample() -> Html {
html! {
<Theme accent_color={AccentColor::Indigo}>
<MyApp />
</Theme>
}
}Available Accent Colors
There is a range of accent colors to choose from:
TODO: visual
Accent Scale Anatomy
Each accent is a 12-step scale that includes a solid and a transparent variant of each color. For example, here’s the AccentColor::Indigo color scale:
TODO: visual
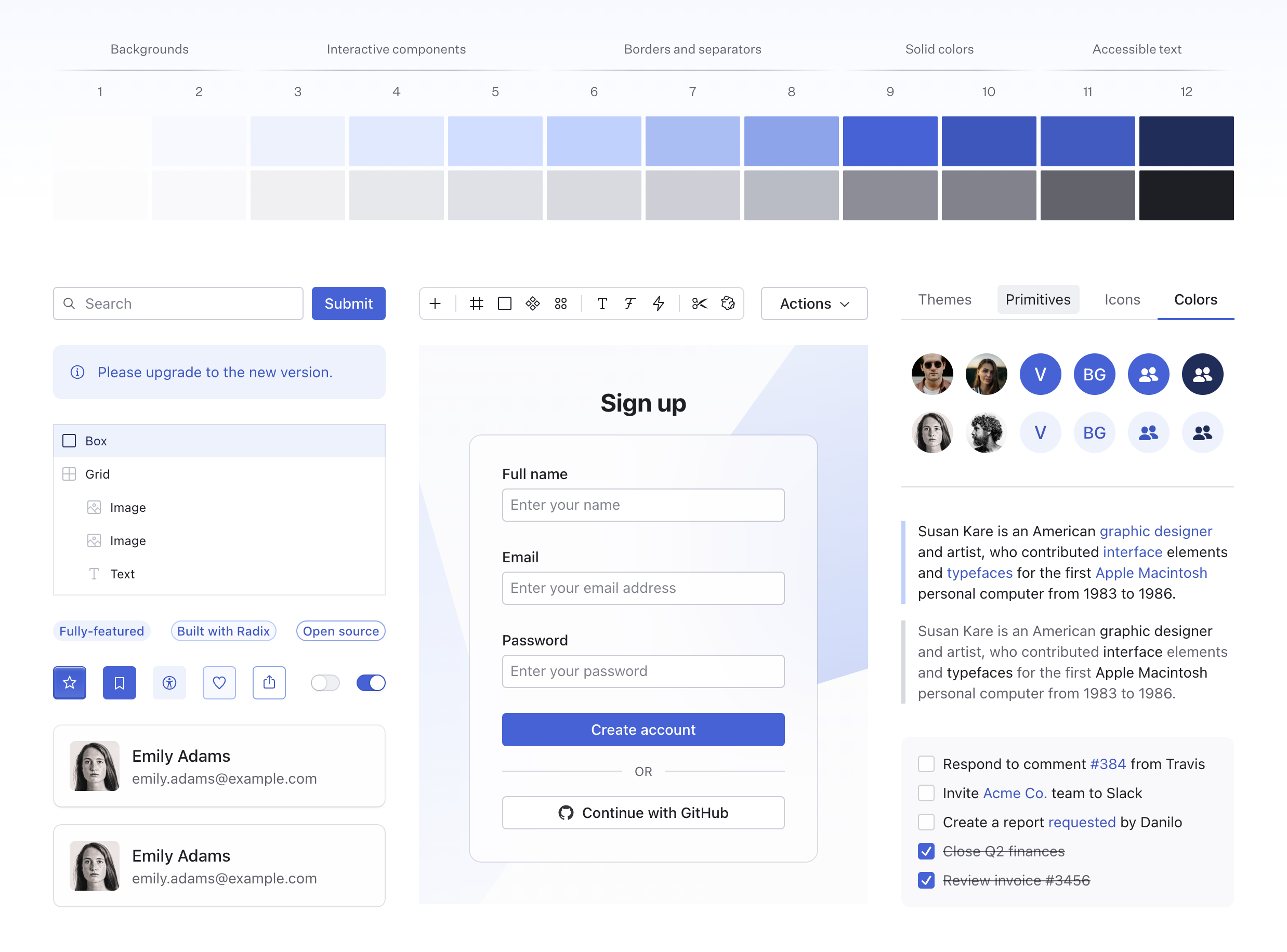
Accent Scale Tokens
Accent color tokens can be accessed using CSS variables. You can use these tokens to style your custom components, ensuring they are accessible and consistent with the rest of your theme.
/* Backgrounds */
var(--accent-1);
var(--accent-2);
/* Interactive components */
var(--accent-3);
var(--accent-4);
var(--accent-5);
/* Borders and separators */
var(--accent-6);
var(--accent-7);
var(--accent-8);
/* Solid colors */
var(--accent-9);
var(--accent-10);
/* Accessible text */
var(--accent-11);
var(--accent-12);
/* Functional colors */
var(--accent-surface);
var(--accent-indicator);
var(--accent-track);
var(--accent-contrast);
Grays
You can also choose between a pure gray or a number of tinted grays. Your accent color will be automatically paired with a gray shade that compliments it. However, you can also specify a custom gray_color directly on the Theme component:
use radix_yew_themes::{GrayColor, Theme};
use yew::prelude::*;
#[function_component]
pub fn GrayColorExample() -> Html {
html! {
<Theme gray_color={GrayColor::Mauve}>
<MyApp />
</Theme>
}
}Available Gray Colors
There is 6 grays to choose from. The difference may seem subtle, but it is impactful especially on pages with a lot of text or in dense UIs.
TODO: visual
Gray Scale Anatomy
Grays are based on the same 12-step color scale that includes a solid and a transparent variant of each color. For example, here’s the Gray::Slate color scale:
TODO: visual
Gray Scale Tokens
Gray color tokens can be accessed using CSS variables. You can use these tokens to style your custom components, ensuring they are accessible and consistent with the rest of your theme.
/* Backgrounds */
var(--gray-1);
var(--gray-2);
/* Interactive components */
var(--gray-3);
var(--gray-4);
var(--gray-5);
/* Borders and separators */
var(--gray-6);
var(--gray-7);
var(--gray-8);
/* Solid colors */
var(--gray-9);
var(--gray-10);
/* Accessible text */
var(--gray-11);
var(--gray-12);
/* Functional colors */
var(--gray-surface);
var(--gray-indicator);
var(--gray-track);
var(--gray-contrast);
Color Overrides
When available, the color prop on the components can be used to override the theme accent. Nested components will automatically inherit the new accent color.
TODO: example
Individual Color Tokens
Individual colors can be accessed directly using similar CSS variables by their corresponding names. For example, the reds are accessed via --red-1, --red-2, and so on up to --red-12.
High Contrast
Most of the time, components with a color prop also provide a high_contrast option that achieves appearance that stands out against the page background:
TODO: example
Focus and Selection
Radix Themes automatically adjusts the focus and selection colors depending on the accent color of the current component. Most of the time, setting the color prop will intelligently change the focus and selection colors to avoid a mismatch of conflicting hues:
TODO: example
Focus Scale Tokens
Focus color tokens can be accessed using CSS variables that follow a similar naming structure like the other scales, e.g. --focus-1, --focus-2, and so on up to --focus-12.
Most of the components use --focus-8 for the focus outline color.
Alpha Colors
Every color has an alpha variant which is designed to appear visually the same when placed over the page background. This is a powerful tool that allows colors to look naturally when overlayed over another background. All numerical color steps have a corresponding alpha variant.
/* Solid colors */
var(--red-1);
var(--red-2);
...
var(--red-12);
/* Alpha colors */
var(--red-a1);
var(--red-a2);
...
var(--red-a12);
Alpha colors are used automatically within Radix Themes components - no additional configuration is required.
Backgrounds
A number of background colors are used to create a sense of visual hierarchy in Radix Themes UIs. These colors are used for backgrounds, cards, and other surfaces.
/* Page background */
var(--color-background);
/* Panel backgrounds, such as cards, tables, popovers, dropdown menus, etc. */
var(--color-panel-solid);
var(--color-panel-translucent);
/* Form component backgrounds, such as text fields, checkboxes, select, etc. */
var(--color-surface);
/* Dialog overlays */
var(--color-overlay);
Panel Background
The panel_background prop controls whether panelled elements use a solid or a translucent background color. The default PanelBackground::Translucent value creates a subtle overlay effect:
use radix_yew_themes::{PanelBackground, Theme};
use yew::prelude::*;
#[function_component]
pub fn PanelBackgroundExample() -> Html {
html! {
<Theme panel_background={PanelBackground::Translucent}>
<MyApp />
</Theme>
}
}TODO: example
While PanelBackground::Solid is useful when you’d prefer to present information unobstructed.
use radix_yew_themes::{PanelBackground, Theme};
use yew::prelude::*;
#[function_component]
pub fn PanelBackgroundExample() -> Html {
html! {
<Theme panel_background={PanelBackground::Solid}>
<MyApp />
</Theme>
}
}TODO: example
Customization
Radix Themes colors can be customized by overriding the corresponding CSS variables of the token system. Refer to the source code for the full list of the color tokens.
Make sure that your CSS is applied after the Radix Themes styles so that it takes precedence.
Brand Color
You can replace a specific color with your brand color by remapping the corresponding token. Usually, you’d override step 9 of the scale that you are using as your theme accent.
.radix-themes {
--my-brand-color: #3052f6;
--indigo-9: var(--my-brand-color);
--indigo-a9: var(--my-brand-color);
}
In this example, using solid-colored AccentColor::Indigo components will now reference your custom color.
Custom Palette
You can use the custom color palette tool to generate a custom palette based just on a couple reference colors. Once you are happy with the result, paste the generated CSS into your project. You can rename the generated colors to match the accent that you want to use in your theme.
To generate dark theme colors, toggle the appearance to use the dark theme. Make sure to paste the generated CSS after your light theme color overrides.
Color Aliasing
You may prefer to use generic color names to refer to the color shades that you want to use. For example, it is common to refer to AccentColor::Crimson, AccentColor::Jade, and AccentColor::Indigo as AccentColor::Red, AccentColor::Green, and AccentColor::Blue respectively.
In this case, you can remap Radix Themes tokens in place of one another and reclaim the color names you want to use:
.radix-themes {
--red-1: var(--ruby-1);
--red-2: var(--ruby-2);
--red-3: var(--ruby-3);
--red-4: var(--ruby-4);
--red-5: var(--ruby-5);
--red-6: var(--ruby-6);
--red-7: var(--ruby-7);
--red-8: var(--ruby-8);
--red-9: var(--ruby-9);
--red-10: var(--ruby-10);
--red-11: var(--ruby-11);
--red-12: var(--ruby-12);
--red-a1: var(--ruby-a1);
--red-a2: var(--ruby-a2);
--red-a3: var(--ruby-a3);
--red-a4: var(--ruby-a4);
--red-a5: var(--ruby-a5);
--red-a6: var(--ruby-a6);
--red-a7: var(--ruby-a7);
--red-a8: var(--ruby-a8);
--red-a9: var(--ruby-a9);
--red-a10: var(--ruby-a10);
--red-a11: var(--ruby-a11);
--red-a12: var(--ruby-a12);
--red-surface: var(--ruby-surface);
--red-indicator: var(--ruby-indicator);
--red-track: var(--ruby-track);
--red-contrast: var(--ruby-contrast);
}
In this example, using the AccentColor::Red color in Radix Themes components and tokens would now reference the original AccentColor::Ruby scale.
Individual CSS Files
Color definitions comprise around 20% of the total CSS size that Radix Themes ships with.
If you’d prefer to reduce your CSS bundle size and have access just to the colors you use, you can import the individual CSS files for each color module. Here’s a sample setup:
// Base theme tokens
@import "@radix-ui/themes/tokens/base.css";
// Include just the colors you use, for example `ruby`, `teal`, and `slate`.
// Remember to import the gray tint that matches your theme setting.
@import "@radix-ui/themes/tokens/colors/ruby.css";
@import "@radix-ui/themes/tokens/colors/teal.css";
@import "@radix-ui/themes/tokens/colors/slate.css";
// Rest of the CSS
@import "@radix-ui/themes/components.css";
@import "@radix-ui/themes/utilities.css";
Please note that the colors you didn’t import will still be accepted by the color prop in Rust. Also, make sure that your developer tooling preserves the order of the imported CSS files.